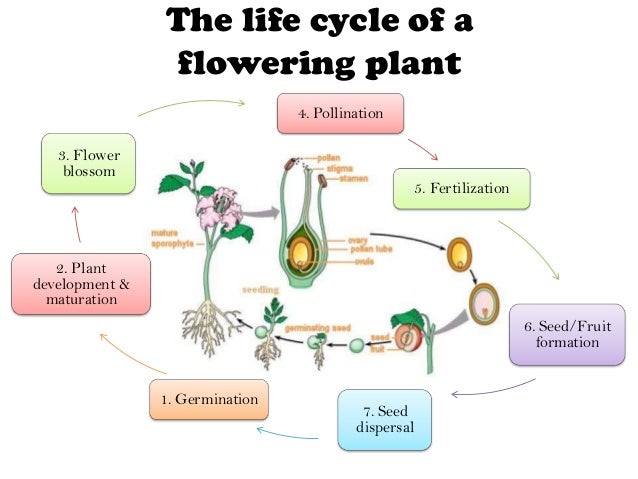
Or what methods do they adopt for reproduction?Reproduction in plants Germination is a process, controlled by enzymes, in which the seed begins to develop into a new young plant Three mainThe phenomenon of Seed Dispersal helps in reproduction in plants But what ex Ever wondered how seeds from one Plant get sown in a different area altogether?
Pmr Form 3 Science Chapter 4 Plant Reproduction
Reproduction in flowerless seed plants
Reproduction in flowerless seed plants- · Modes Of Reproduction in Plants There are several ways by which plants produce their offspring These are categorised into two types (i) asexual, and (ii) sexual In asexual reproduction plants can give rise to new plants without seeds, whereas in sexual reproduction, new plants are obtained from seedsHowever, the underlying mechanisms remain to be fully elucidated This review summarizes findings that reveal the importance and complexity of the role of peroxisomes in the pertinent processes



Part 3 Growth Reproduction And Evolution Plant Reproduction Aceites Esenciales Dōterra
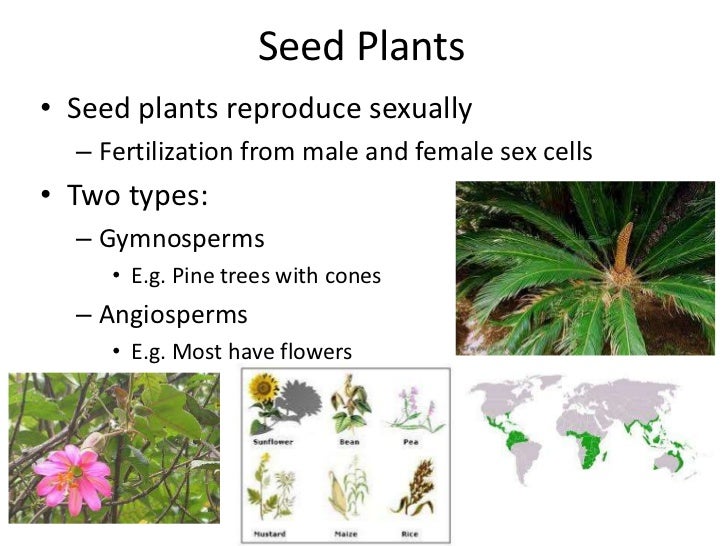
· Recruitment, establishment and survivorship of seed and vegetativelyderived shoots were quantified biweekly in annually burned and infrequently burned tallgrass prairie to investigate the contributions of seed and vegetative reproduction to the maintenance and dynamics of tallgrass prairie plant populations, the demography of seedlings and ramets, and the influence0704 · Plant reproduction refers to production of new offspring in plants which can be either asexual or sexual methods Sexual reproduction is the production of new offspring by the fusion of gametes and produces offspring genetically different from the parents · Most plants grow from seeds These seed plants fall into two groups, angiosperms and gymnosperms Angiosperms are the flowering plants Their seeds develop inside a female reproductive part of the flower, called the ovary, which usually ripens into a protective FRUITGymnosperms (conifers, Ginkgo, and cycads) do not have flowers or ovaries
2610 · This seed, when under favourable conditions of soil, water and air, develops into a seedling, a process known as germination This germinated seedling further is involved in the development of new plant This way, the seed helps in reproduction ←The formation of the seed completes the process of reproduction in plants (started with the development of flowers and pollination), with the embryo developed from the zygote and the seed · In addition, reproductive efficiency in seed plants is largely influenced by life form and breeding system (Sutherland and Delph, 1986, Sutherland, 1986, Ramírez, 1993) lifeform is intimately related to photosynthetic pathway (Medina, 1995, Ehleringer, 1995, Wang, 05) and succulence is closely related to CAM species (McWilliams, 1970, Kluge and Ting, 1978,
• 3) If seed plants were homosporous, what aspects of their reproduction would change?Grasses, tulips, and potatoes may produce seeds, but more commonly reproduce by sprouting from underground stems The offspring of these plants are clones of the parent plant The underground, reproductive stems take different forms depending on the plant In grasses, these stems, called rhizomes, grow out from the parent plant and1500 · Plant reproductive system, any of the systems, sexual or asexual, by which plants reproduce Asexual reproduction results in offspring that are identical to the parent plant Sexual reproduction involves new genetic combinations and results in offspring that are genetically different from the parent plants




4 Germination Sexual Reproduction In Plants




Plant Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Some Plants Produce New
· These sexual reproduction in flowering plants class 12 mcqs are compiled from NEET, AIIMS and JIPMER previous years question paper and NCERT Let's discuss about the Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class 12 Quizes 1 Corn cob tussles are made up of · Almost all plants reproduce by sexually formed seeds, but they often complement reproduction by seed with clonal (asexual) reproduction, most often by stolons, rhizomes or similar organs capable of rooting and/or resprouting and forming new fully functional individuals (Mogie & Hutchings 1990;0221 · Q1 The production of new plants from a single parent without the involvement of gametes is called _____ reproduction a) asexual b) sexual c) none Q2 In sexual reproduction, new plants are obtained from existing plants through _____ a) roots b) stems c) seeds Q3 Spirogyra reproduces by the method of _____




9 4 Reproduction In Plants Sl Hl Biology




P5 Science Reproduction In Flowering Plants By Audrey Gan
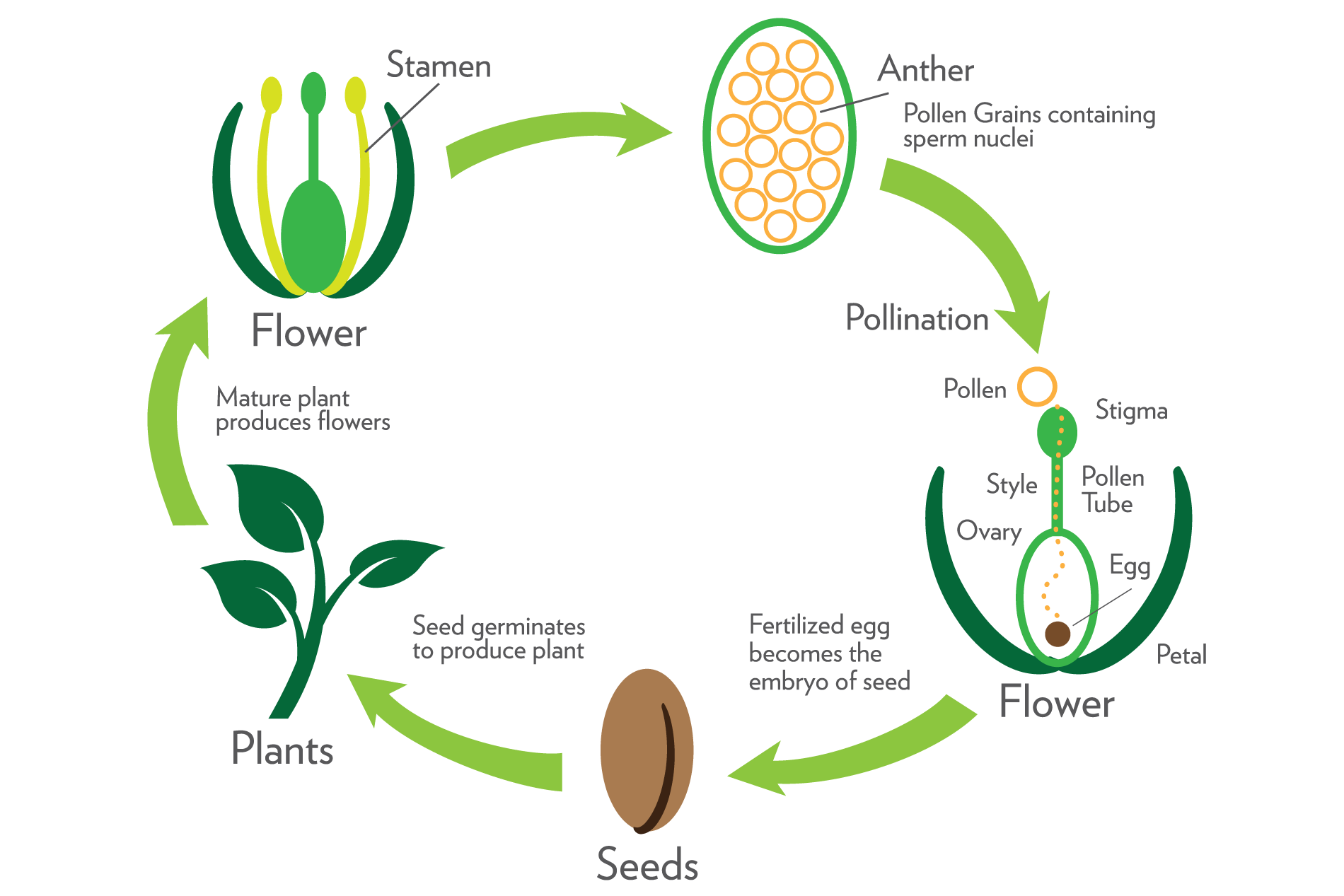
· Both seeds and pollen distinguish seed plants from seedless vascular plants These innovative structures allowed seed plants to reduce or eliminate their dependence on water for gamete fertilization and development of the embryo, and to conquer dry land Pollen grains are male gametophytes, which contain the sperm (gametes) of the plant · Way by which plant reproduce their young ones Sexual reproduction flowering plants make use of seeds In most plants, the seedlings are developed from their seeds, which is obtained from flower when the male and female parts of flower meet to form union, seeds are obtained from flowerAlthough plants can reproduce by other natural means, eg by seeds or by any of the abovementioned methods, man sometimes cuts the leaves or stems of plants and places them in either soil or water so that they can grow into new plants The new plants will have identical characteristics to their parent plants new plant develops from




Fun Germination Facts For Kids



Tomatosphere Tomatosphere The Life Cycle Of A Tomato Plant
Plant reproduction is the process by which plants generate new individuals, or offspring Reproduction is either sexual or asexual Sexual reproduction is the formation of offspring by the fusion of gametes Asexual reproduction is the formation ofWell, plants reproduce by several methods They can be asexual as well as sexual To our surprise, there is an additional method of reproduction called "Vegetative Reproduction" in plants Sounds interesting, right? · The importance of plant peroxisomes in reproduction, seed development, seed germination and early seedling establishment is clearly demonstrated by peroxisome mutant analyses Multiple peroxisome pathways are involved and some pathways affect more than one developmental process, thus forming a complex network of functional connections




Plant Propagation Sexual Reproduction Of Plants Ppt Download



Flowering Plant Reproduction
Mutant analysis demonstrated key roles for peroxisomes in plant reproduction, seed development and germination and postgerminative seedling establishment;Reproduction In Plants 12 Videos 0042 Hours Share Ever wondered how plants reproduce? · Reproduction in plants Sexual reproduction produces offspring that are not identical to their parents, whereas asexual reproduction produces identical offspring Part of




Reproduction In Plants Class 7 Science Seed Dispersal Youtube




How Do Seed Plants Grow Reproduce
· Dispersal Of Seeds and Fruits Dispersal of seeds means to scatter seeds over a wide area The seeds of some of the plants such (as seeds) but the seeds of other plants disperse in the form of fruits (because fruits contain seeds inside them) The same kind of plants (and trees) grow at different places because their seeds are dispersed to different places by the variousPlants with sperm delivery in seed plants • 2) What additional features of seed plants, not present in seedless plants, have contributed to the enormous success of seed plants on land?About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators



How Seep Plants Reproduce Study Sheet Hanford Christian School Jane Kitson




How To Grow From Seed The Garden Of Eaden
1701 · Flowering plants reproduce sexually through a process called pollination The flowers contain male sex organs called stamens and female sex organs called pistils The anther is the part of the stamen that contains pollen This pollen needs to · Ans Sexual reproduction is a process which involves production of seeds It requires two parents Most plants reproduce sexually with the help of flowers The main function of a flower is to reproduce and therefore develop new seeds that can grow into new plants Q4 State the main difference between asexual and sexual reproduction• Throughout history, people have relied on seeds and plant parts to grow new plants for food and fiber • In more recent times, knowledge of plant reproduction has resulted in the development of plant hybrids that have enabled large scale agricultural production of food and fiber plants



Plant Reproduction Seed Plants



Asexual Reproduction Biology Ii
Seed predation selects for reproductive variability and synchrony in perennial plants Michał Bogdziewicz1, Jakub Szymkowiak2, Andrew J Tanentzap3, Rafael Calama4, Shealyn Marino5, Michael A Steele5, Barbara Seget6, Łukasz Piechnik6 and Magdalena Zywiec_ 6 1Department of Systematic Zoology, Faculty of Biology, Adam Mickiewicz University, Ul UniwersytetuSeed, the characteristic reproductive body of both angiosperms (flowering plants) and gymnosperms (eg, conifers, cycads, and ginkgos) Essentially, a seed consists of a miniature undeveloped plant (the embryo), which, alone or in the company of stored food for its early development after germination, isIn sexual reproduction, the offspring of a plant is identical to one of the parents only All plants reproduce by either sexual or asexual reproduction A zygote is formed during the process of fertilization Reproduction in a plant results in the formation of a new plant



Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub




Flowering Plants Reproduction Worksheet
· Evolution of Seed Plants The lush palms on tropical shorelines do not depend upon water for the dispersal of their pollen, fertilization, or the survival of the zygote, unlike mosses, liverworts, and ferns of the terrain Seed plants, such as palms, have broken free from the need to rely on water for their reproductive needs · Fragmentation – A new plants are developed from fragments of the parent plant Apomixis – it is the type of asexual reproduction in which seeds are formed and the embryo is developed without the fusion of male and female gametes Citrus trees commonly use this method of asexual reproduction by using their seeds · This special issue focuses on diverse aspects of plant reproduction, including apomixis and sexual plant reproduction, germline identity, plant domestication, and fruit ripening From the moment that a plant switches from vegetative to reproductive growth through to when a seed is finally formed, an intricate network of signalling and regulatory pathways are activated




Fun Germination Facts For Kids



Flowering Plant Reproduction
The earliest seed plants, "progymnosperms", emerged in the late Devonian (see figure below) Progymnoperm fossils show vegetative morphologies to seed plants, but not all progymnosperms had seeds or seedlike structures (ovules or preovules) Archaeopteris spp was the first modern tree, but it sproduced spores rather than seeds · Sexual reproduction in plants The flower is the reproductive organ of the plant It usually contains male organs (pollen containing pollen containing sperm) and female organs (an ovary containing eggs, from which leaves a leaf and a scar in the head) After fertilization, ovulation with the eggs develops into fruit with seedsSome winddispersed seeds could fall in water or on stones, for example



Reproduction In Plants



1
· The Hard seed coat provides protection to the embryo Produce new genetic combinations leading to variations, as they are the product of sexual mode of reproduction Seed Viability Ability of seed to remain alive after their dispersal It can be a few months to several years Name part B of the stamen and give its role in the sexual reproduction of plants Give a way in which the pollen from the flower of one plant can be transferred to the flower of another plant Name the cell that is formed when a male gamete (sperm) and a female gamete (egg) combineWant to Reproduction In Plants




Pin On Science Lessons
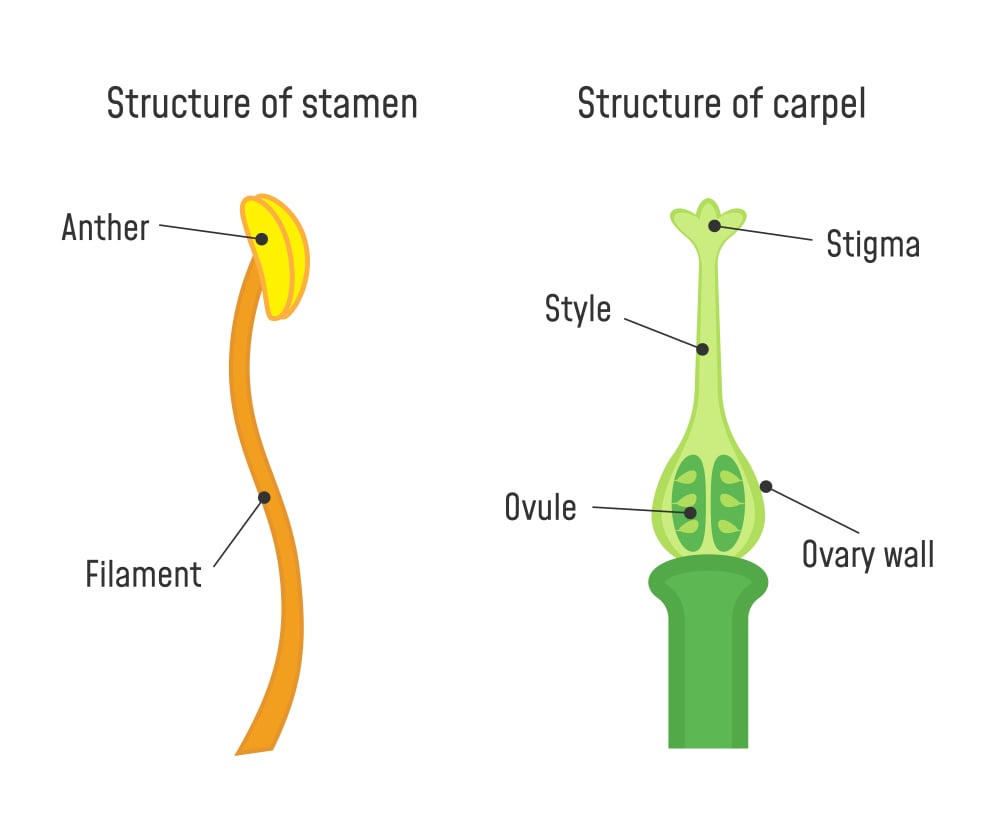



Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce
In plants, reproduction is carried out via two modes Asexual Mode – New plants are obtained without producing seeds Sexual Mode – New plants are obtained from seedsEvolution of Seed Plants The lush palms on tropical shorelines do not depend upon water for the dispersal of their pollen, fertilization, or the survival of the zygote, unlike mosses, liverworts, and ferns of the terrain Seed plants, such as palms, have broken free from the need to rely on water for their reproductive needsSeed Germination Plants produce many fruits and therefore many seeds This is because only a few of these seeds will find suitable places and conditions in which to germinate The majority of the seeds will be wasted;




Part 3 Growth Reproduction And Evolution Plant Reproduction Aceites Esenciales Dōterra




Learnhive Cbse Grade 5 Science Reproduction In Plants Lessons Exercises And Practice Tests
How Do Plants Reproduce Reproduction of Corn The fertilized ovule will become one of the seeds of the tomato fruit The seed contains the embryo and the endosperm and is covered by a strong seed coat, called the testa The testa is unique to tomatoes The seed forms a thick outer epidermal layer




Plant Reproduction Seed Plants
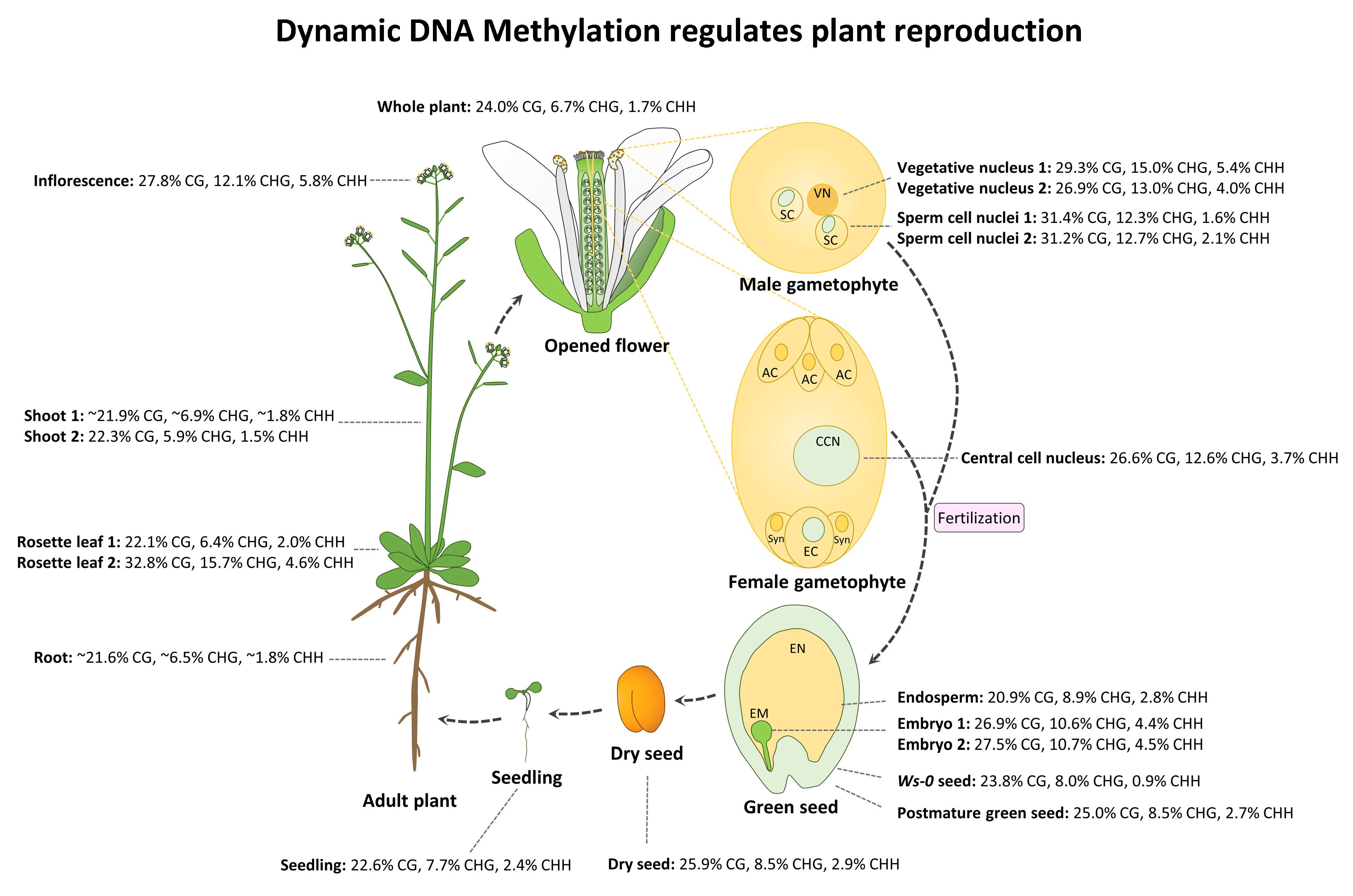



Plants Free Full Text Epigenetics Regulates Reproductive Development In Plants




Sexual Reproduction In Plants The Seed The Seed Is The Product Of Sexual Reproduction In Most Plants The Seed Contains An Embryo A Food Supply Ppt Download
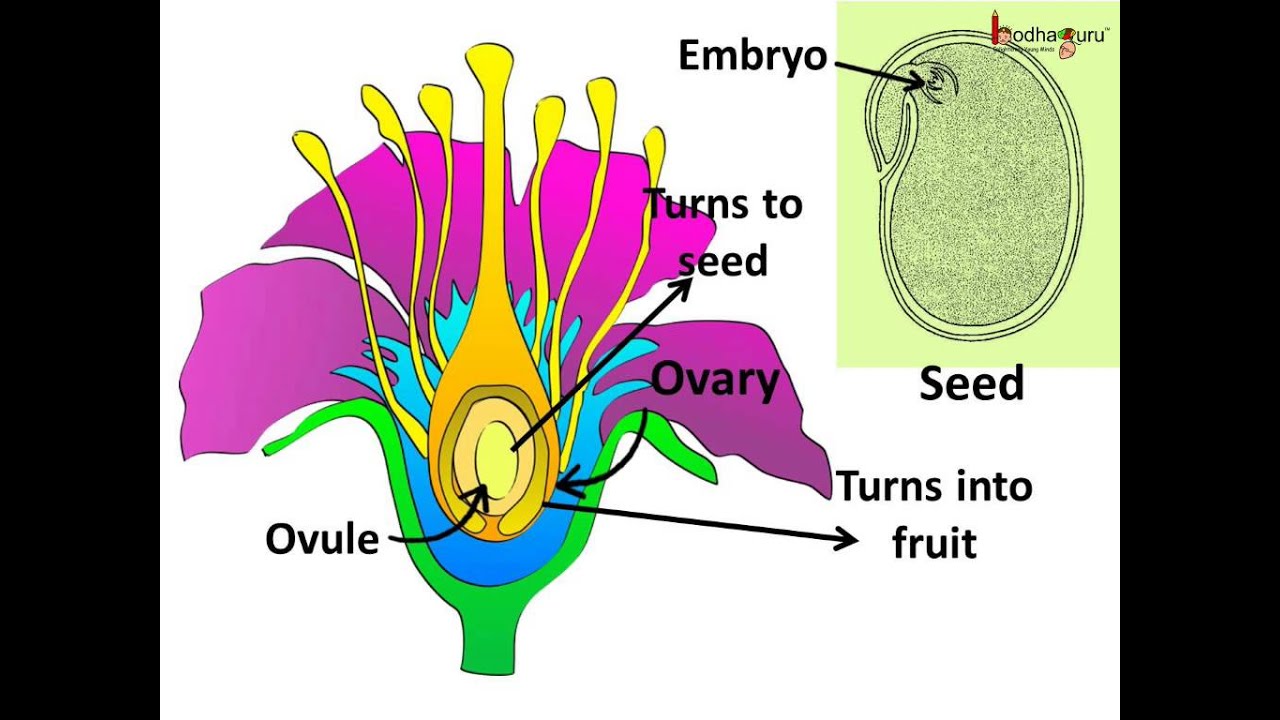



Science Sexual Reproduction In Plants Pollination Fertilization Hindi Youtube
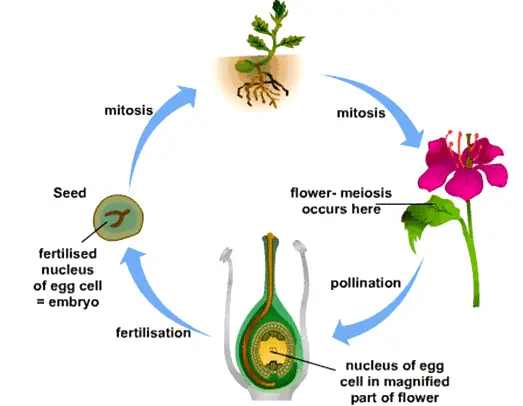



Ncert Class 7 Science Twelfth Chapter Reproduction In Plants Exercise Solutions




Ppt Chapter 24 Reproduction Of Seed Plants Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




13 3 Sexual Reproduction In Seed Plants




Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S




5 Reproduction Of Plants How Do Plants Reproduce




1 Seed Formation Sexual Reproduction In Plants




Class 5th Science Reproduction In Plants Chapter 1 Youtube




Reproduction In Living Things Braintor Library




Plant Reproduction Worksheet Teachers Pay Teachers




Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub
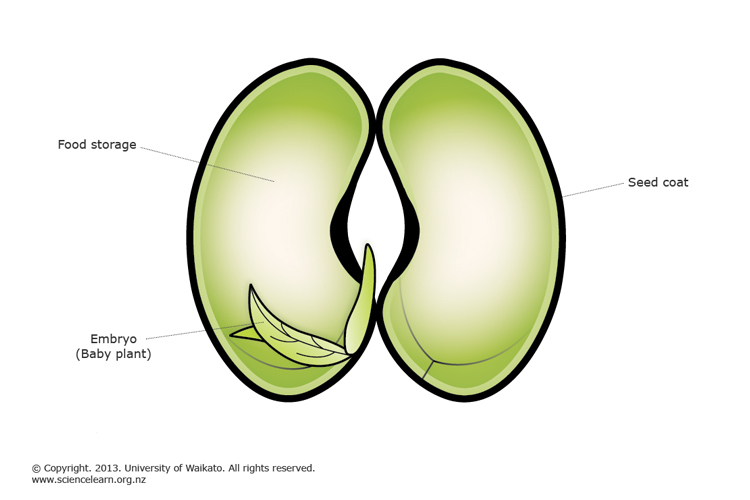



Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




Outdoor Education School Science Camps California




Plant Reproduction Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii




Seed Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help




Reproduction System Reproduction Systems In Plants Seed Propagated
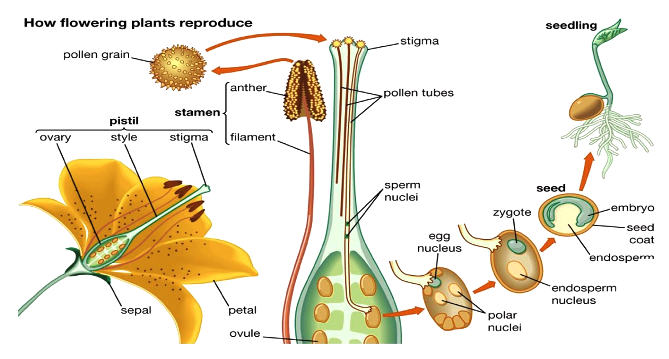



Learn About Flowering Plant Reproduction Chegg Com
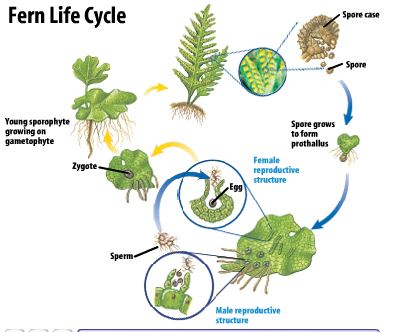



Sexual Reproduction Grade 11 University Biology



Plant Reproduction Biology Junction




Seed Dispersal Interactive Worksheet




Pmr Form 3 Science Chapter 4 Plant Reproduction
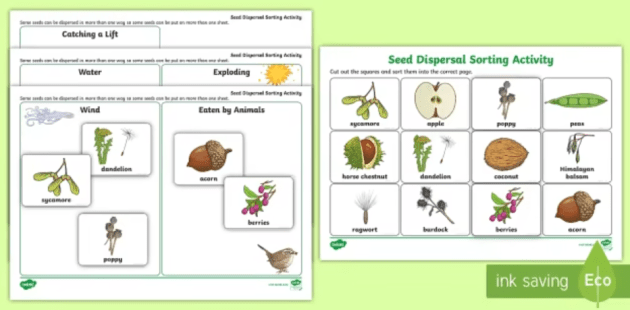



What Is Reproduction In Plants Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




719 Plant Reproduction Stock Vector Illustration And Royalty Free Plant Reproduction Clipart
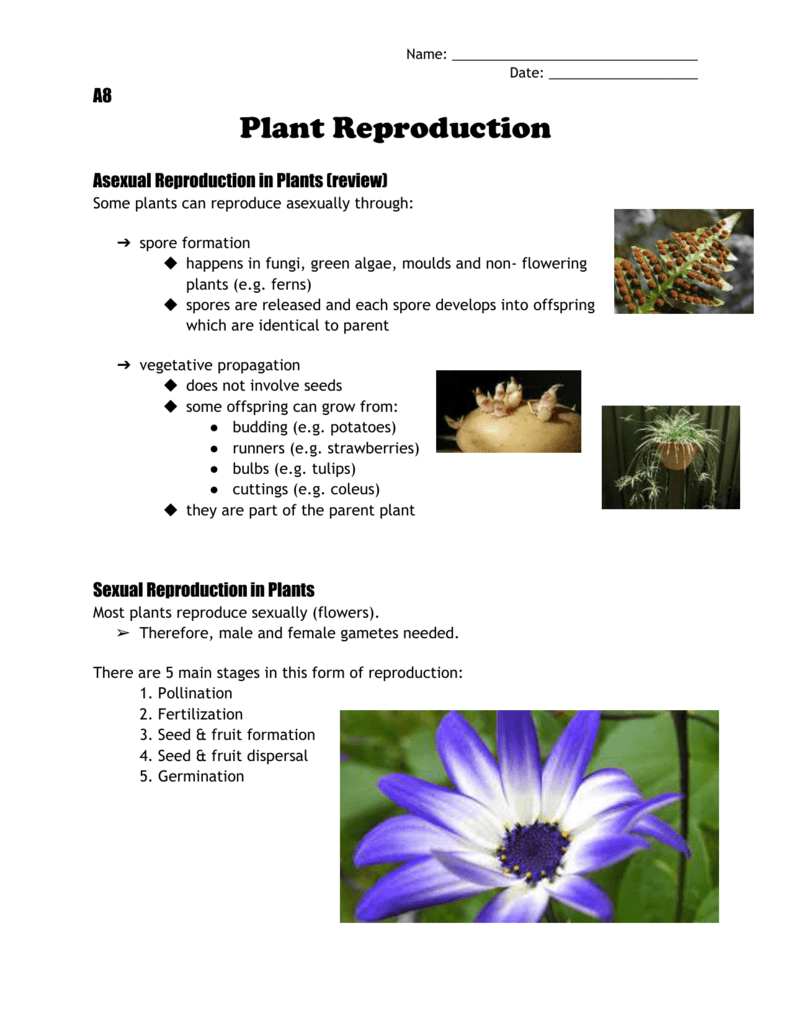



12 Plant Reproduction




Pin On Fruit Seeds




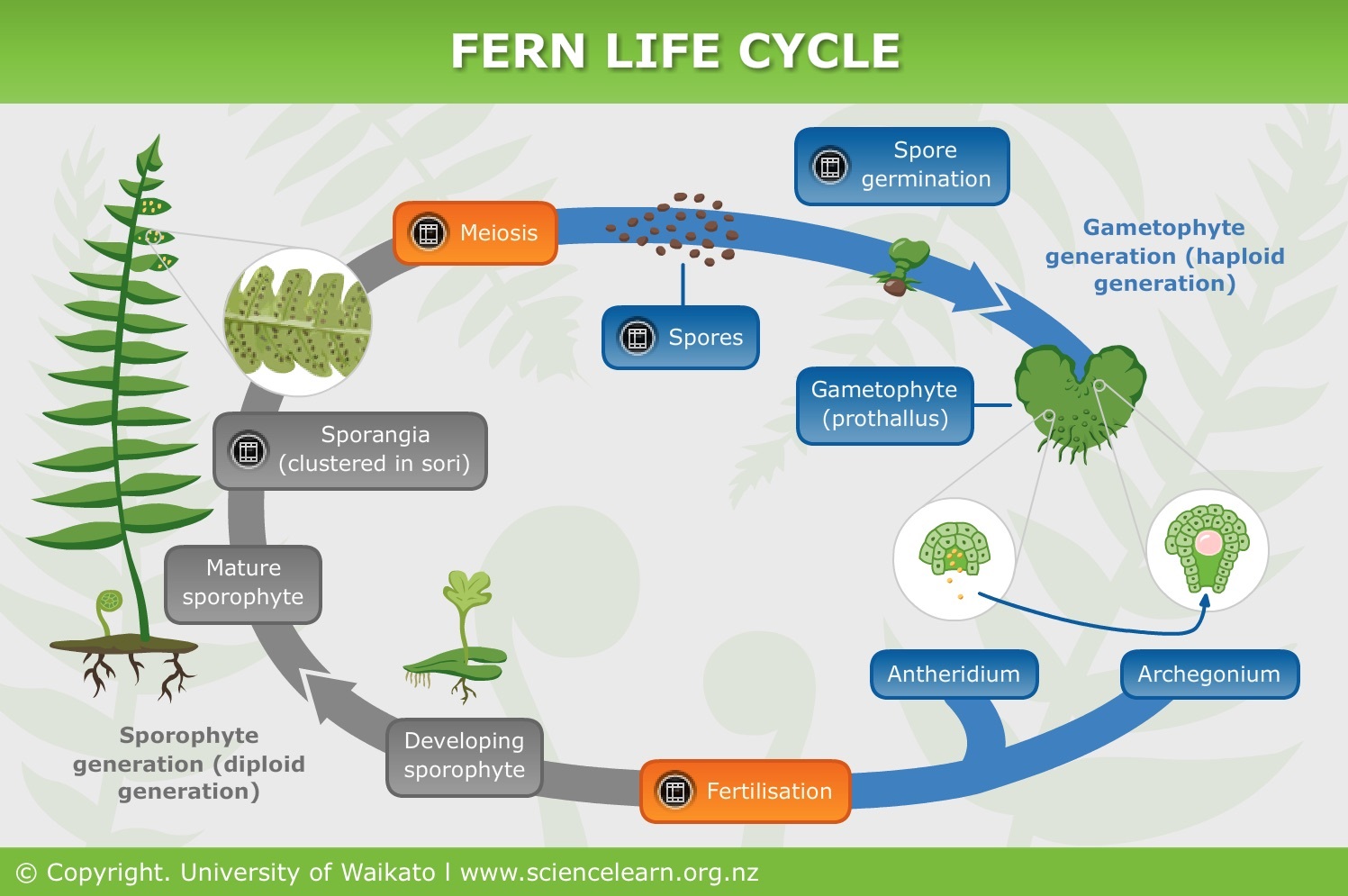
Fern Reproduction Seed Less Vascular Plants Diagram Quizlet
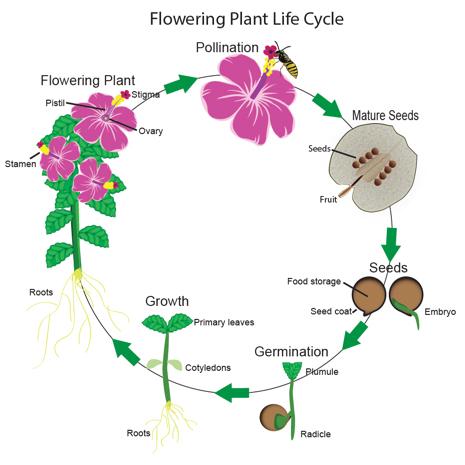



Flowering Plants Life Cycle Lovetoknow




Plant Reproduction Seed Plants
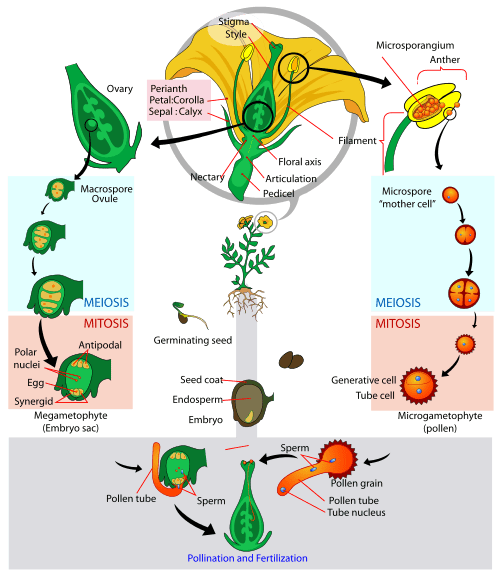



Plant Reproduction Organismal Biology




Learnhive Cbse Grade 5 Science Reproduction In Plants Lessons Exercises And Practice Tests



Reproduction In Plants Psle Science
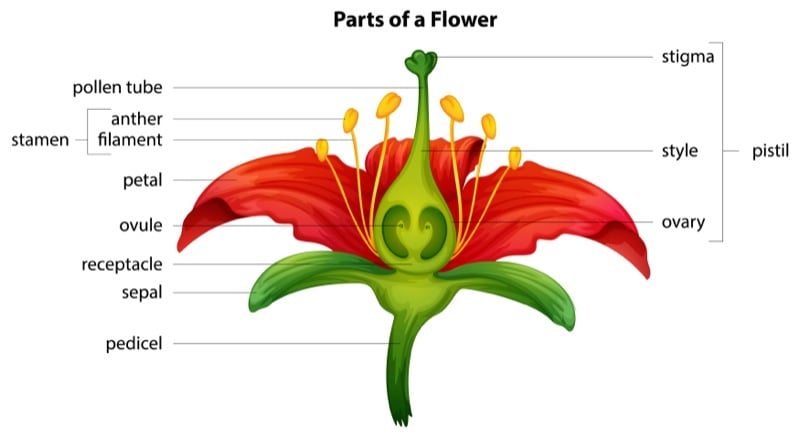



Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce
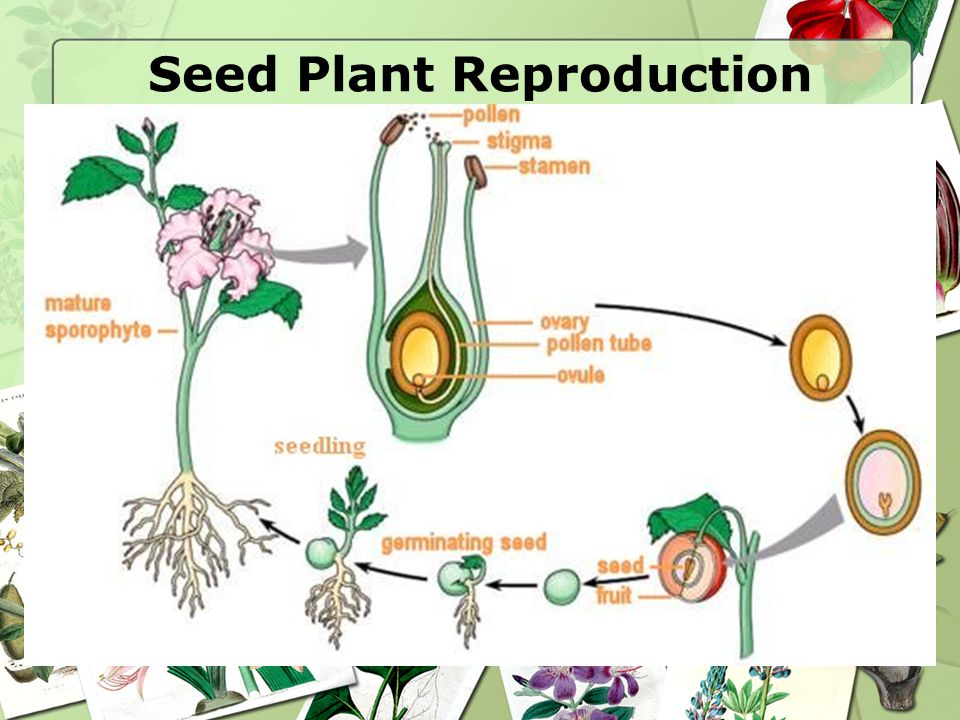



3 2 Notes Plant Reproduction Ppt Download




Life Cycle Of Plants Easy Review How They Grow And What Is Their Cycle



1
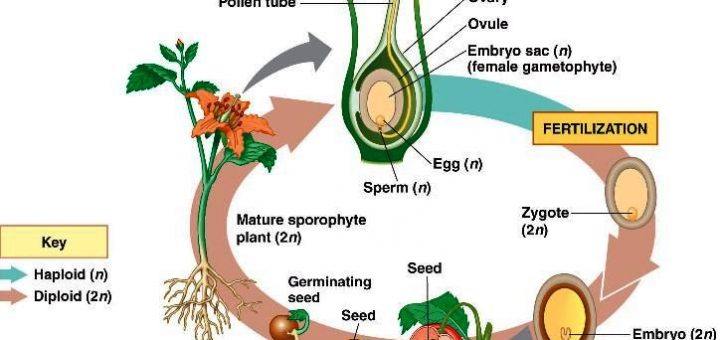



Sexual Reproduction In Plants Science Online
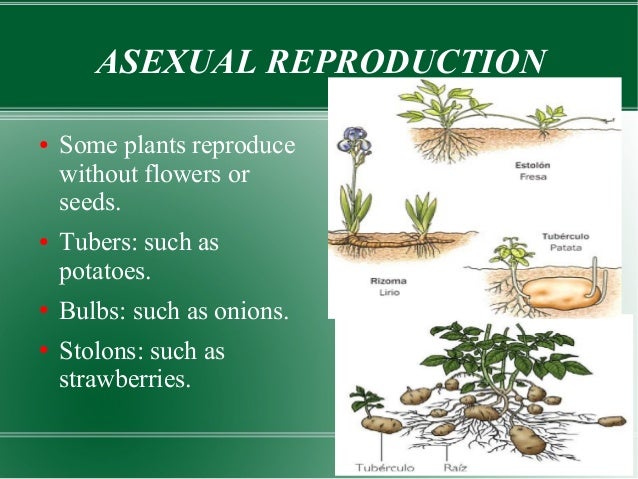



Plant Reproduction



Plos One Spatial Niche Facilitates Clonal Reproduction In Seed Plants Under Temporal Disturbance




Reproduction In Plants Class 5 Worksheet




Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants S Cool The Revision Website



1




Plant Reproduction Bioninja
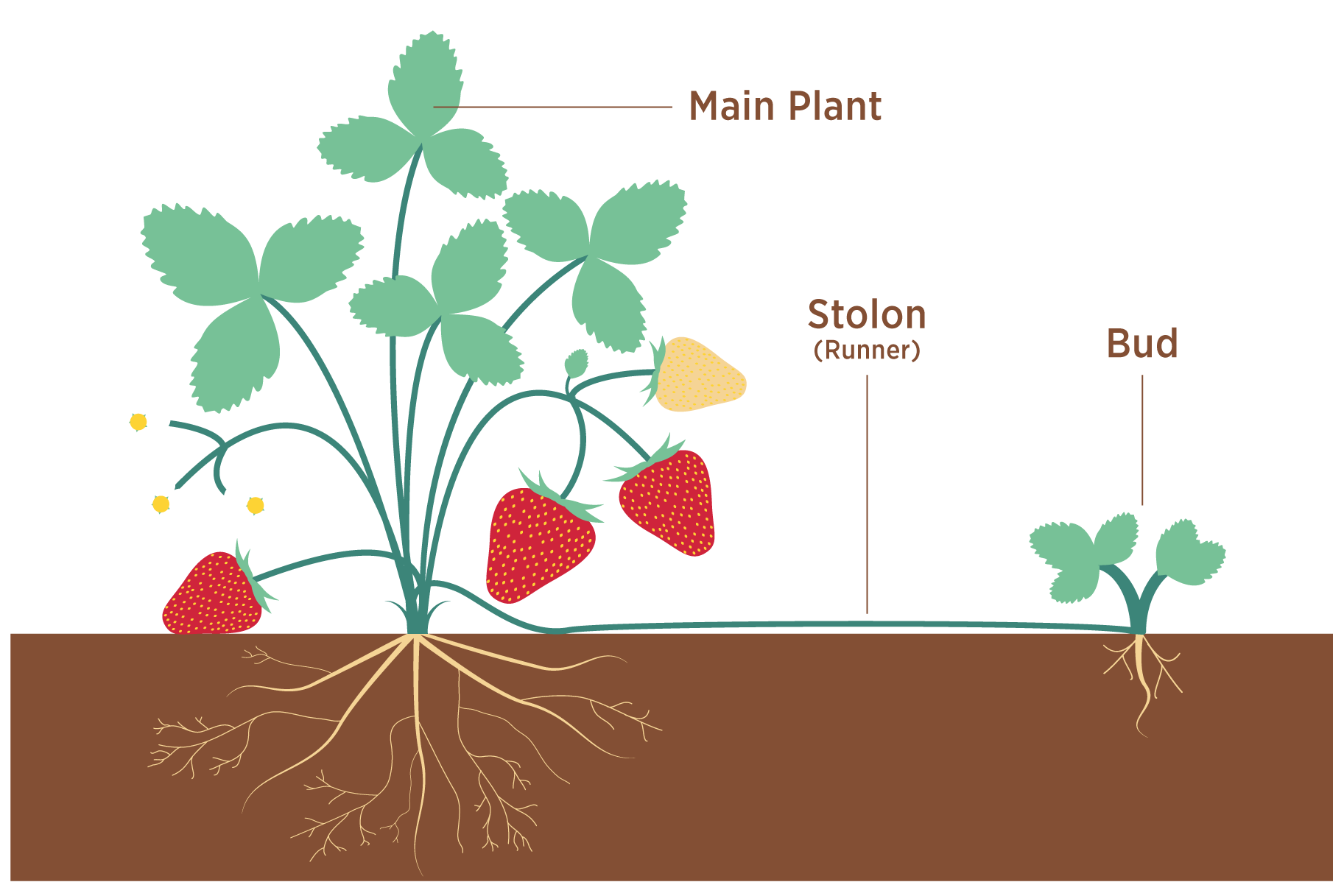



Part 3 Growth Reproduction And Evolution Plant Reproduction Dōterra Essential Oils



Plant Reproduction Biology Junction




Plant Propagation Wikipedia




Ovary Botany Definition Structure Britannica




Plant Reproduction



How Do Plants Reproduce Sexually B4fa



Flowering Plant Reproduction




Plant Reproductive Development And Structure Boundless Biology
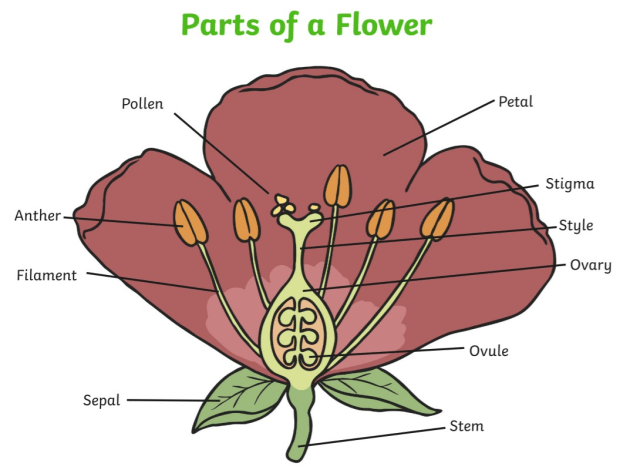



What Is Reproduction In Plants Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




Plant Reproduction Sexual And Asexual Teaching Resources




Learn Characteristics Of Living Organisms Nutrition Growth Reproduction And Lifespan In 3 Minutes




Vegetative Propagation Using Plant Cuttings To Reproduce Existing Plants




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica




Biology Sexual Reproduction In Plants Part 18 Seed Monocot Dicot Structure Class 12 Xii Youtube




Science Plant Reproduction Seed Dispersal Germination English Youtube



1




Plant Reproduction Plants




Introduction To Reproduction In Plants Don T Memorise Youtube
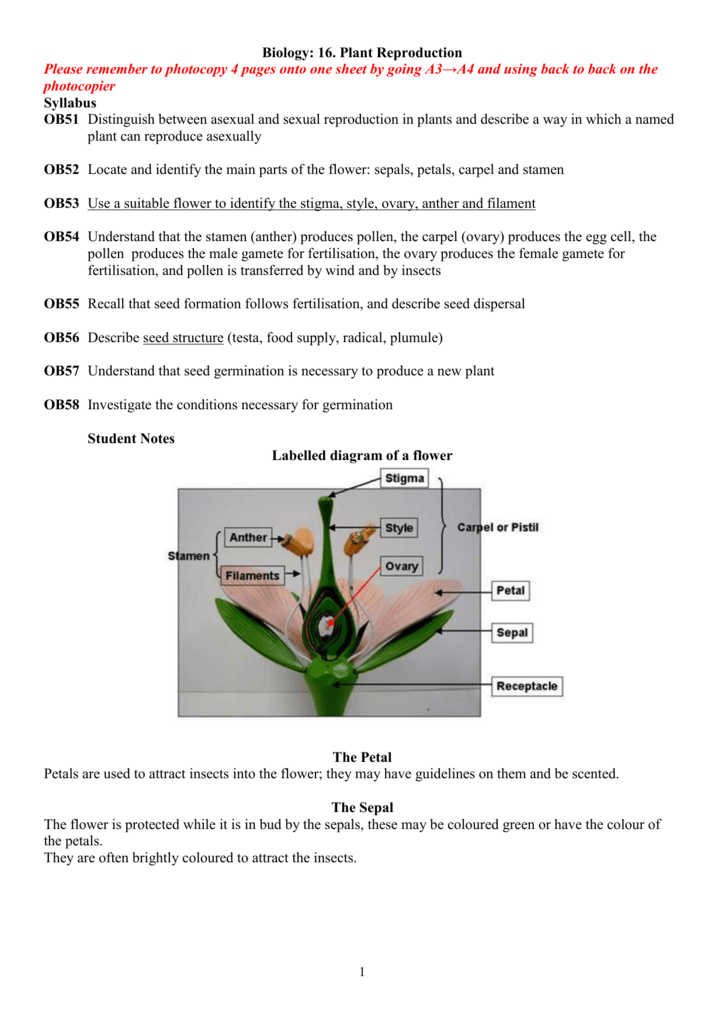



16 Plant Reproduction
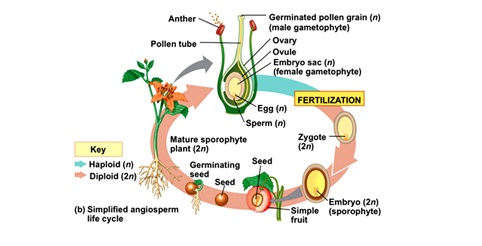



How Do Organisms Reproduce Tutormate




9 4 Reproduction In Plants Sl Hl Biology
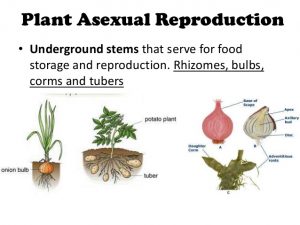



Advantages And Disadvantages Of Asexual Reproduction In Plants Science Online
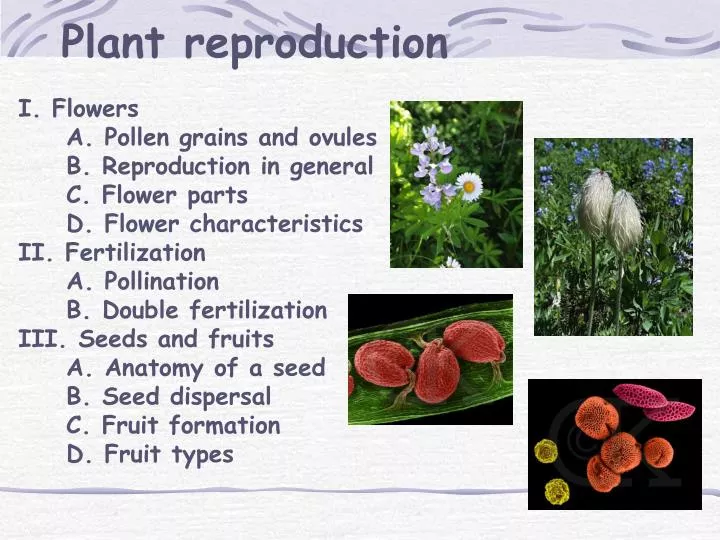



Ppt Plant Reproduction Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Plant Reproductive System Angiosperms Britannica
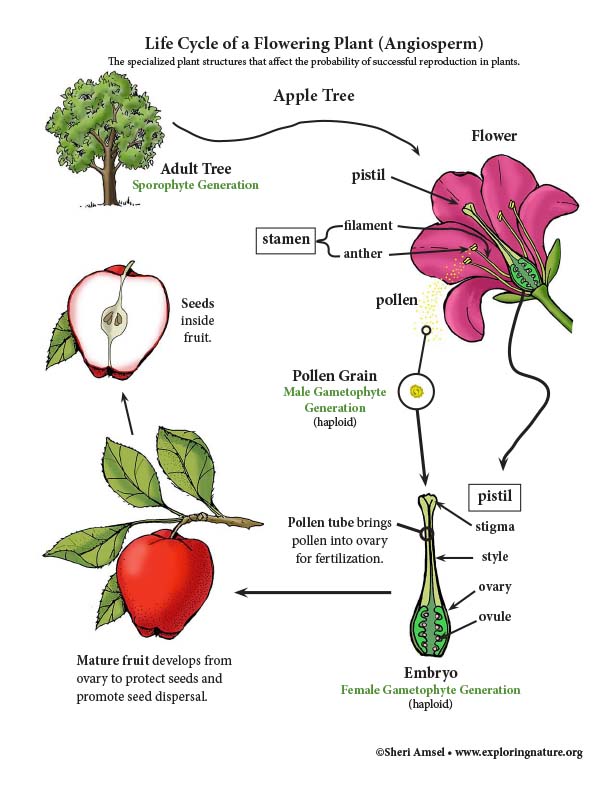



Plant Reproduction Illustrated Growth And Development Of Organisms Ngss 6 8 Grade
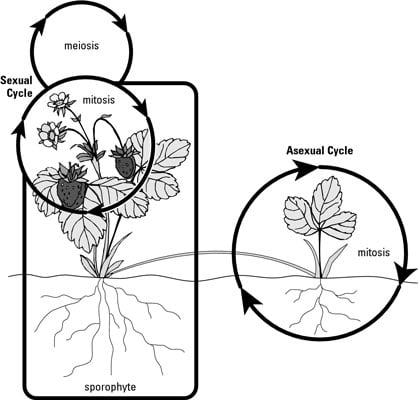



Plant Reproduction Dummies
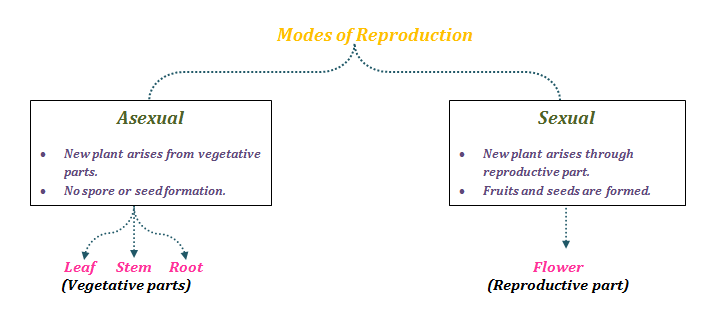



Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S
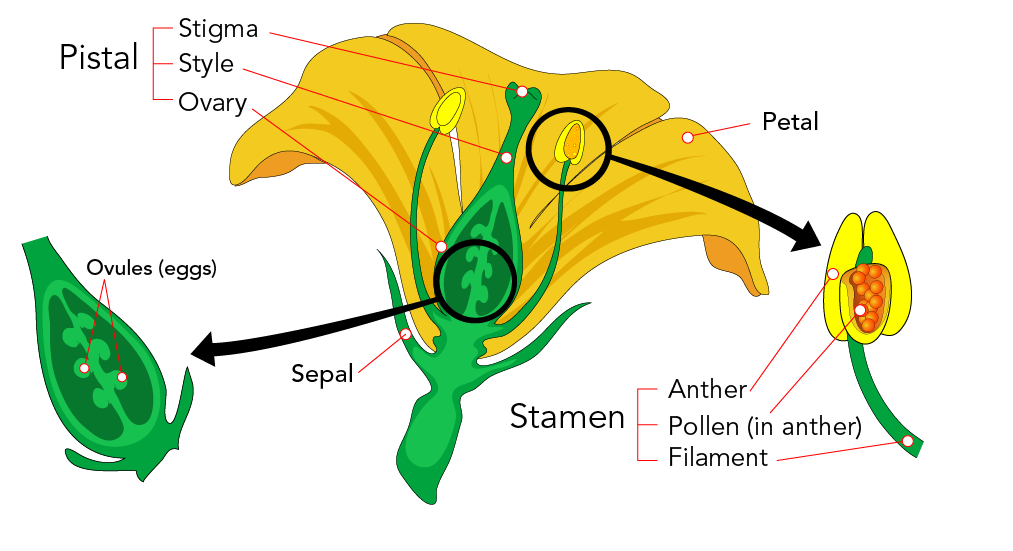



Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




Reach For The Sun Lesson 3 Plant Life Cycles And Reproduction Filament Games
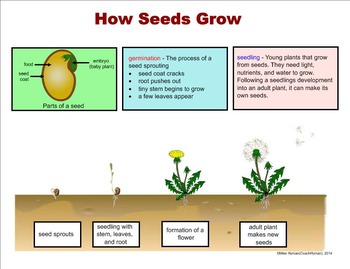



Seed Plant Reproduction A Fourth Grade Smartboard Introduction By Mike Hyman
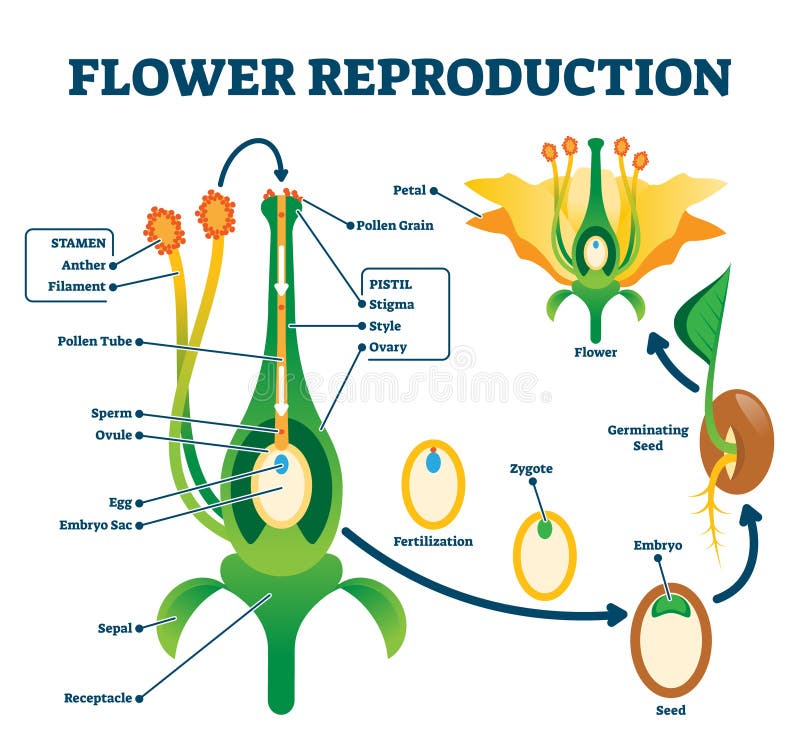



Plants Reproduction Stock Illustrations 247 Plants Reproduction Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
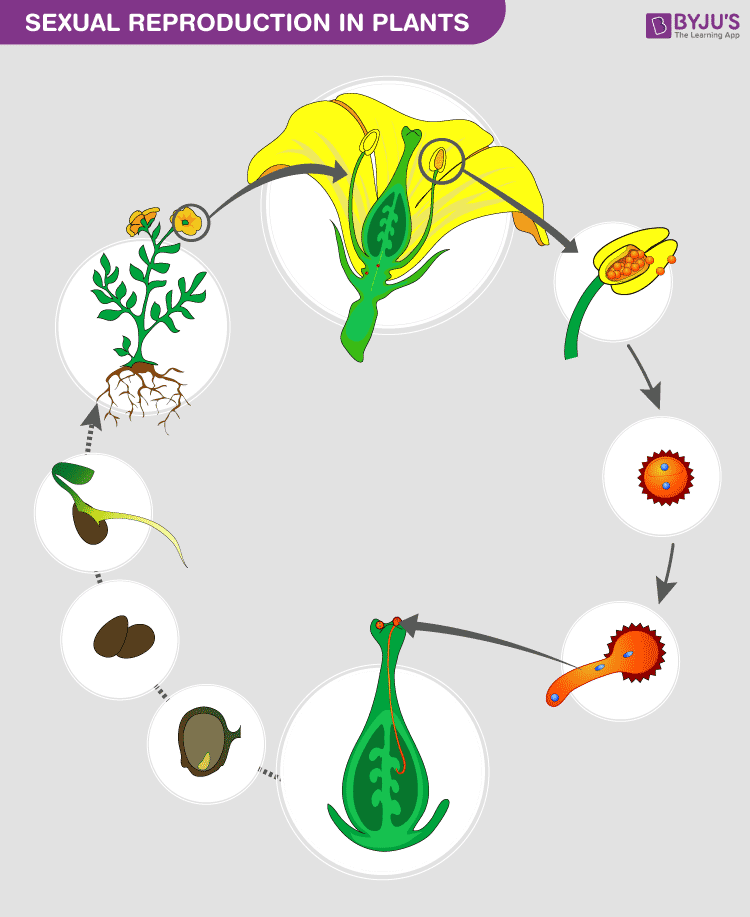



Sexual Reproduction In Plants Features And Its Process




Plant Reproduction Wikipedia



How Do Organisms Reproduce Tutormate



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿